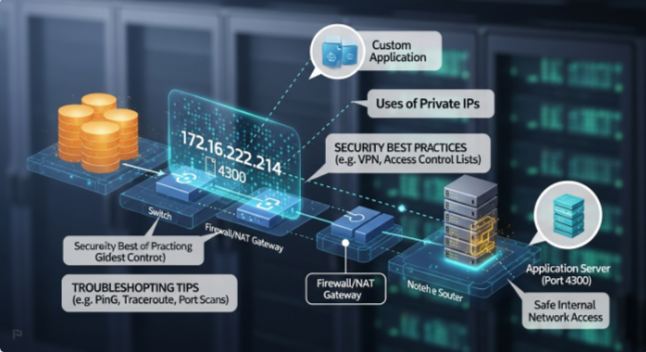
In the modern digital landscape, understanding IP addresses and ports is crucial for IT professionals, network administrators, and cybersecurity enthusiasts. One IP that often comes under scrutiny in internal networks is 172.16.252.214, particularly when accessed through port 4300. This guide explores everything you need to know about 172.16.252.214:4300, including its network classification, potential applications, security implications, and practical use cases. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how this IP and port function, as well as best practices for securing and using them effectively.
What is 172.16.252.214?
Understanding Private IP Addresses
172.16.252.214 is a private IP address that falls within the 172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255 range, which is reserved for private networks according to RFC 1918. Private IP addresses are not routable on the public internet and are primarily used within internal networks, such as corporate LANs, home networks, and VPNs.
Key characteristics of 172.16.252.214 include:
-
IP Class: B (Class B private network)
-
Network Range: 172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255
-
Default Subnet Mask: 255.240.0.0
-
Purpose: Internal communication within a private network
This IP is often assigned to a device using Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) or manually configured for static network purposes.
What is Port 4300?
Ports are endpoints in a network that allow applications to communicate over IP addresses. Port 4300 is considered a non-standard port, meaning it doesn’t have a widely recognized default service like HTTP (port 80) or HTTPS (port 443). Organizations often use ports like 4300 for custom applications, private servers, or testing purposes.
Common uses of port 4300:
-
Custom Web Services – Some internal applications host dashboards or APIs on non-standard ports to avoid conflicts.
-
Game Servers – Certain gaming or simulation platforms may use higher-numbered ports like 4300.
-
Development and Testing – Developers may assign port 4300 for testing APIs locally or in private networks.
-
IoT Devices – Smart devices sometimes use unconventional ports for internal communication.
How 172.16.252.214:4300 is Used
Internal Networking
The combination 172.16.252.214:4300 is typically used in private networks for connecting devices and services. Examples include:
-
Internal company dashboards: Employees access internal tools without exposing them to the public internet.
-
Testing servers: Developers use internal IPs with custom ports to test software in a safe environment.
-
IoT communication: Smart sensors, cameras, or controllers may communicate over private IPs with specific ports.
Remote Access and VPNs
When paired with a VPN (Virtual Private Network), 172.16.252.214:4300 can provide secure remote access to internal services. VPN solutions allow users to connect to private IPs as if they were on the same local network, which is ideal for:
-
Remote development teams
-
Secure access to internal databases
-
Administration of internal servers
Security Implications of 172.16.252.214:4300
Although private IP addresses like 172.16.252.214 are not exposed to the internet, improper configuration can still create security risks:
-
Open Ports – If port 4300 is left open without authentication, unauthorized users could exploit services.
-
Misconfigured Firewalls – Failing to restrict access to trusted devices can lead to potential breaches.
-
Internal Threats – Insider attacks or compromised devices on the same network could misuse services on port 4300.
-
Unencrypted Communication – Data sent over unencrypted channels can be intercepted within the internal network.
Security best practices for 172.16.252.214:4300:
-
Use firewall rules to restrict access to trusted devices.
-
Enable authentication on services running on port 4300.
-
Employ encryption (TLS/SSL) even for internal traffic.
-
Monitor network traffic for unusual activity using IDS/IPS systems.
-
Regularly update the software or services running on this port to patch vulnerabilities.
How to Access 172.16.252.214:4300 Safely
Step 1: Confirm Internal Network Access
Ensure your device is connected to the same private network or VPN. Private IPs like 172.16.252.214 cannot be accessed from the public internet.
Step 2: Use Appropriate Tools
-
Web browser – If the service is web-based, type
http://172.16.252.214:4300. -
SSH/Telnet client – For command-line access, connect via SSH or Telnet if supported.
-
Network scanner – Tools like Nmap can verify if port 4300 is open and which service is running.
Step 3: Authenticate and Secure
Always use credentials, API keys, or tokens required by the service running on port 4300. Avoid exposing these to shared networks.
Troubleshooting 172.16.252.214:4300 Connectivity Issues
Even within private networks, users can experience connectivity problems. Common issues include:
-
Port Closed or Blocked – Ensure firewall settings allow traffic to port 4300.
-
IP Conflicts – Two devices on the same network should not share the same IP address.
-
Service Not Running – Confirm the application or service on port 4300 is active.
-
VPN Configuration – Check VPN settings if accessing remotely.
-
Subnet Mismatch – Ensure your device is on the same subnet or routing is properly configured.
Pro Tip: Use ping 172.16.252.214 to verify network connectivity and telnet 172.16.252.214 4300 to test port access.
Potential Applications for Businesses
Businesses often leverage private IPs and non-standard ports like 4300 for:
-
Internal dashboards: Monitoring servers, employee management, and analytics.
-
Database management: Running internal SQL or NoSQL servers safely inside a private network.
-
Custom APIs: Securely exchanging data between internal applications.
-
IoT management: Controlling smart office systems like thermostats, cameras, or lighting.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Regular monitoring of 172.16.252.214:4300 is essential to ensure network stability and security:
-
Port Scanning – Schedule regular scans to detect unauthorized open ports.
-
Traffic Logging – Keep logs of access attempts and monitor for unusual patterns.
-
Service Updates – Update applications to prevent vulnerabilities from being exploited.
-
Firewall Rules Review – Periodically check that only authorized devices can access this IP and port.
Difference Between Private and Public IP Access
Private IPs (like 172.16.252.214):
-
Only accessible inside local networks or via VPN.
-
Safer from external attacks if properly configured.
-
Common for development, testing, and internal communication.
Public IPs:
-
Accessible from anywhere on the internet.
-
Require strong security protocols.
-
Often exposed to scanning and hacking attempts.
Understanding the distinction ensures you configure network devices and applications correctly.
Advanced Tips for Network Administrators
-
Port Forwarding – If external access is required, carefully set up port forwarding on your router.
-
Network Segmentation – Separate sensitive services from general internal networks.
-
Use Non-Standard Ports – Using ports like 4300 can reduce automated attacks but does not replace authentication.
-
VPN-only Access – Restrict access to private IPs through VPNs for remote workers.
Summary
The combination 172.16.252.214:4300 represents a private IP and non-standard port, commonly used for internal networking, testing, and custom applications. While it is inherently safe from public internet threats, improper configuration can still lead to vulnerabilities. Understanding its functionality, use cases, and security practices is essential for IT professionals, network administrators, and even home network enthusiasts.
By following best practices—such as firewalls, authentication, monitoring, and VPN access—you can ensure 172.16.252.214:4300 remains a secure and effective part of your network infrastructure.